learn-redux
coderhyh 1/9/2023 笔记redux
# 为什么需要redux
- JavaScript开发的应用程序,已经变得越来越复杂了:
- JavaScript需要管理的状态越来越多,越来越复杂
- 这些状态包括服务器返回的数据、缓存数据、用户操作产生的数据等等,也包括一些UI的状态,比如某些元素是否被选中,是否显示加载动效,当前分页
- 管理不断变化的state是非常困难的:
- 状态之间相互会存在依赖,一个状态的变化会引起另一个状态的变化,View页面也有可能会引起状态的变化
- 当应用程序复杂时,state在什么时候,因为什么原因而发生了变化,发生了怎么样的变化,会变得非常难以控制和追踪
- React是在视图层帮助我们解决了DOM的渲染过程,但是State依然是留给我们自己来管理:
- 无论是组件定义自己的state,还是组件之间的通信通过props进行传递;也包括通过Context进行数据之间的共享
- React主要负责帮助我们管理视图,state如何维护最终还是我们自己来决定
- Redux就是一个帮助我们管理State的容器:Redux是JavaScript的状态容器,提供了可预测的状态管理
- Redux除了和React一起使用之外,它也可以和其他界面库一起来使用(比如Vue),并且它非常小(包括依赖在内,只有2kb)
# Redux的核心理念
# Store
- Redux的核心理念非常简单
- 比如我们有一个朋友列表需要管理
- 如果我们没有定义统一的规范来操作这段数据,那么整个数据的变化就是无法跟踪的
- 比如页面的某处通过friends.push的方式增加了一条数据
- 比如另一个页面通过friends[0].age = 25修改了一条数据
- 整个应用程序错综复杂,当出现bug时,很难跟踪到底哪里发生的变化
const state = {
friends: [
{ name: 'hyh', age: 21 }
]
}
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
# action
- Redux要求我们通过action来更新数据:
- 所有数据的变化,必须通过派发(dispatch)action来更新
- action是一个普通的JavaScript对象,用来描述这次更新的type和content
- 比如下面就是几个更新friends的action
- 强制使用action的好处是可以清晰的知道数据到底发生了什么样的变化,所有的数据变化都是可跟追、可预测的
const nameAction = { type: "change_name", name: "kobe" }
store.dispatch(nameAction)
console.log(store.getState())
const nameAction2 = { type: "change_name", name: "lilei" }
store.dispatch(nameAction2)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
# reducer
但是如何将state和action联系在一起呢?答案就是reducer
- reducer是一个纯函数
- reducer做的事情就是将传入的state和action结合起来生成一个新的state
function reducer(state = initialState, action) { switch(action.type) { case 'change_name': return { ...state, name: action.name } case 'add_number': return { ...state, counter: state.counter + action.num } default: return state } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# Redux的三大原则
- 单一数据源
- 整个应用程序的
state被存储在一颗object tree中,并且这个object tree只存储在一个store中 - Redux并没有强制让我们不能创建多个Store,但是那样做并不利于数据的维护
- 单一的数据源可以让整个应用程序的state变得方便维护、追踪、修改
- 整个应用程序的
- State是只读的
- 唯一修改
State的方法一定是触发action,不要试图在其他地方通过任何的方式来修改State - 这样就确保了
view或网络请求都不能直接修改state,它们只能通过action来描述自己想要如何修改state - 这样可以保证所有的修改都被集中化处理,并且按照严格的顺序来执行,所以不需要担心
race condition(竟态)的问题
- 唯一修改
- 使用纯函数来执行修改
- 通过
reducer将 旧state和actions联系在一起,并且返回一个新的State - 随着应用程序的复杂度增加,我们可以将
reducer拆分成多个小的reducers,分别操作不同state tree的一部分 - 但是所有的
reducer都应该是纯函数,不能产生任何的副作用
- 通过
# Redux的基本使用
初始化
reduxconst { createStore } = require("redux") const reducer = require("./reducer.js") // 创建的store const store = createStore(reducer) module.exports = store1
2
3
4
5
6
7创建
Store来存储这个state- 创建
store时必须创建reducer - 可以通过
store.getState来获取当前的state
// constants.js const ADD_NUMBER = "add_number" const CHANGE_NAME = "change_name" module.exports = { ADD_NUMBER, CHANGE_NAME }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8// reducer.js const { ADD_NUMBER, CHANGE_NAME } = require("./constants") // 初始化的数据 const initialState = { name: "hyh", counter: 100 } function reducer(state = initialState, action) { switch(action.type) { case CHANGE_NAME: return { ...state, name: action.name } case ADD_NUMBER: return { ...state, counter: state.counter + action.num } default: return state } } module.exports = reducer1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20- 创建
通过
action来修改state- 通过
dispatch来派发action - 通常
action中都会有type属性,也可以携带其他的数据
// actionCreators.js const { ADD_NUMBER, CHANGE_NAME } = require("./constants") const changeNameAction = (name) => ({ type: CHANGE_NAME, name }) const addNumberAction = (num) => ({ type: ADD_NUMBER, num }) module.exports = { changeNameAction, addNumberAction }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17const store = require("./store") const { addNumberAction, changeNameAction } = require("./store/actionCreators") const unsubscribe = store.subscribe(() => { console.log("订阅数据的变化:", store.getState()) }) // 修改store中的数据: 必须action store.dispatch(changeNameAction("kobe")) store.dispatch(changeNameAction("lilei")) store.dispatch(changeNameAction("james")) // 取消订阅 unsubscribe() // 修改counter store.dispatch(addNumberAction(10)) store.dispatch(addNumberAction(20)) store.dispatch(addNumberAction(30))1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18- 通过
# Redux结构划分
- 如果将所有的逻辑代码写到一起,那么当redux变得复杂时代码就难以维护
- 所以需要将
store、reducer、action、constants拆分成一个个文件 - 创建
store/index.js文件 - 创建
store/reducer.js文件 - 创建
store/actionCreators.js文件 - 创建
store/constants.js文件
- 所以需要将
- 注意:node中对ES6模块化的支持
- 从node v13.2.0开始,node才对ES6模块化提供了支持
- node v13.2.0之前,需要进行如下操作
- 在package.json中添加属性:
"type": "module"; - 在执行命令中添加如下选项:
node --experimental-modules src/index.js
- 在package.json中添加属性:
- node v13.2.0之后,只需要进行如下操作
- 在package.json中添加属性:
"type": "module"
- 在package.json中添加属性:
# redux融入react代码
这是一个点击按钮 数字改变的栗子
import React from "react"; import Home from "./views/home"; import About from "./views/about"; import Profile from "./views/profile"; import { AppWrap } from "./style"; import store from "./store"; class App extends React.PureComponent { constructor() { super(); this.state = { unSubscribe: null, // 1.拿到store初始化的num num: store.getState().num, }; } componentDidMount() { // 2.挂载时 订阅state变化时 让组件更新 const unSubscribe = store.subscribe(() => { this.setState({ num: store.getState().num, }); }); // 3.保存unSubscribe 在卸载组件时取消订阅 this.setState({ unSubscribe }); } componentWillUnmount() { // 4.取消订阅 this.state.unSubscribe?.(); } addNum(num) { store.dispatch({ type: "add_num", num }); } render() { const { num } = this.state; const { addNum } = this; return ( <div> <h2>{num}</h2> <button onClick={() => addNum(1)}>+1</button> <AppWrap size="18"> <Home num={num} addNum={addNum} /> <About /> <Profile /> </AppWrap> </div> ); } } export default App;1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53核心代码主要是两个:
- 在
componentDidMount中订阅数据的变化,当数据发生变化时重新设置num - 在发生点击事件时,调用
store的dispatch来派发对应的action
- 在
但是这样使用太过繁琐,所以下面介绍
react-redux插件
# react-redux使用
安装
npm i react-redux在顶部组件使用高阶组件
import React from "react"; import ReactDOM from "react-dom/client"; import App from "./App"; import { Provider } from "react-redux"; import store from './store' const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById("root")); root.render( // 传入store (底层还是context的value) <Provider store={store}> <App /> </Provider> );1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13在组件中使用
import React, { PureComponent } from 'react' import { connect } from 'react-redux' // 导入connect高阶组件 export class Profile extends PureComponent { static propTypes = {} render() { const { num, subNum } = this.props return ( <div> <div>Profile</div> <h2>{num}</h2> <button onClick={() => subNum(1)}>-1</button> </div> ) } } // 这里写 需要使用store中的数据 // 比如num 这样只有在num的更新的时候 才会重新渲染当前组件 // 其他的state变化时 则不会重新渲染 const mapStateToProps = state => ({ num: state.num }) // 映射dispatch到props中使用 const mapDispatchToProps = dispatch => ({ subNum(num) { dispatch({ type: 'sub_num', num }) } }) export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(Profile)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
# redux中异步操作
把请求的数据需要放到redux时,通常是把请求代码写到action中
// About.jsx import React, { PureComponent } from "react"; import { connect } from "react-redux"; import { fetchBanners } from "../../store/action"; export class About extends PureComponent { componentDidMount() { // 1.挂载组件调用映射的dispatch请求数据 this.props.fetchBanners() } render() { const { num, addNum } = this.props; return ( <div> <div>About</div> <h2>{num}</h2> <button onClick={() => addNum(5)}>+5</button> </div> ); } } const mapStateToProps = (state) => ({ num: state.num, }); const mapDispatchToProps = (dispatch) => ({ addNum(num) { dispatch({ type: "add_num", num }); }, fetchBanners() { // 2.对封装的action传入dispatch函数 fetchBanners(dispatch) } }); export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(About);1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35// actions.js import axios from "axios"; export function fetchBanners(dispatch) { axios.get("http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata").then((res) => { const banners = res.data.data.banner.list; // 请求结束调用传入的dispatch来更新store数据 dispatch({ type: "change_banners", banners }); }); }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# redux-thunk的使用
- 以上的方式是把
dispatch传给了fetchBanners- 这里也可以使用中间件
redux-thunk - 可以让
dispatch接收一个action函数
- 这里也可以使用中间件
- redux-thunk介绍
- 默认情况下的
dispatch(action),action需要是一个JavaScript的对象 redux-thunk可以让dispatch(action),action可以是一个函数- 该函数会被调用,并且会传给这个函数一个
dispatch函数和getState函数- dispatch函数用于我们之后再次派发
action - getState函数考虑到我们之后的一些操作需要依赖原来的状态,用于让我们可以获取之前的一些状态
- dispatch函数用于我们之后再次派发
- 默认情况下的
使用
import { applyMiddleware, createStore } from 'redux'
import thunk from 'redux-thunk';
const initState = {
num: 0,
banners: []
}
function reducer(state = initState, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'add_num':
return { ...state, num: state.num + action.num }
case 'sub_num':
return { ...state, num: state.num - action.num }
case 'change_banners':
return { ...state, banners: action.banners }
default:
return state
}
}
// 需要再此使用thunk中间件
const store = createStore(reducer, applyMiddleware(thunk))
export default store
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
import React, { PureComponent } from "react";
import { connect } from "react-redux";
import { fetchBanners } from "../../store/action";
export class About extends PureComponent {
componentDidMount() {
this.props.fetchBanners()
}
render() {
const { num, addNum } = this.props;
return (
<div>
<div>About</div>
<h2>{num}</h2>
<button onClick={() => addNum(5)}>+5</button>
</div>
);
}
}
const mapStateToProps = (state) => ({
num: state.num,
});
const mapDispatchToProps = (dispatch) => ({
addNum(num) {
dispatch({ type: "add_num", num });
},
fetchBanners() {
// 在这里传一个action函数
// 在内部会自动帮我们调用的
dispatch(fetchBanners)
}
});
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(About);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
// action.js
import axios from "axios";
export function fetchBanners(dispatch, getState) {
axios.get("http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata").then((res) => {
const banners = res.data.data.banner.list;
dispatch({ type: "change_banners", banners });
});
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# redux-devtools
redux可以方便的让我们对状态进行跟踪和调试,那么如何做到呢redux官网为我们提供了redux-devtools的工具- 利用这个工具,我们可以知道每次状态是如何被修改的,修改前后的状态变化等等
使用
import { createStore, applyMiddleware, compose, combineReducers } from "redux" import thunk from "redux-thunk" import reducer from "./reducer" // redux-devtools const composeEnhancers = window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__({trace: true}) || compose; const store = createStore(reducer, composeEnhancers(applyMiddleware(thunk))) export default store1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# redux模块化
代码拆分结构
store ├─index.js ├─reducers.js ├─home | ├─actions.js | ├─constants.js | ├─index.js | └reducer.js ├─common | ├─actions.js | ├─constants.js | ├─index.js | └reducer.js1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13store
// index.js import { applyMiddleware, createStore } from 'redux' import thunk from 'redux-thunk'; import reducer from './reducers'; const store = createStore(reducer, applyMiddleware(thunk)) export default store1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9- redux提供了一个
combineReducers函数可以方便的让我们对多个reducer进行合并
// reducers.js import { combineReducers } from "redux"; import homeReducer from './home'; import commonReducer from './common'; const reducer = combineReducers({ homeInfo: homeReducer, commonInfo: commonReducer }) /* // combineReducers 实现原理(了解) // 不过源码内部肯定做了很多边缘处理 function reducer(state = {}, action) { // 返回一个对象, store的state return { counter: counterReducer(state.counter, action), home: homeReducer(state.home, action), user: userReducer(state.user, action) } } */ export default reducer1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25- redux提供了一个
home
// index.js import homeReducer from './reducer'; export * from './constants' export * from './actions' export default homeReducer1
2
3
4
5
6// reducer.js import { ADD_NUM, SUB_NUM } from './constants'; const initState = { num: 0 } function reducer(state = initState, action) { switch (action.type) { case ADD_NUM: return { ...state, num: state.num + action.num } case SUB_NUM: return { ...state, num: state.num - action.num } default: return state } } export default reducer1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19// actions.js import { ADD_NUM, SUB_NUM } from "./constants"; export const addNum = num => ({ type: ADD_NUM, num }) export const subNum = num => ({ type: SUB_NUM, num })1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10// constants.js export const ADD_NUM = 'add_num' export const SUB_NUM = 'sub_num'1
2
3
# Redux Toolkit
- Redux Toolkit 是官方推荐的编写 Redux 逻辑的方法。
- 学习Redux的时候已经发现,redux的编写逻辑过于的繁琐和麻烦
- 并且代码通常分拆在多个文件中(虽然也可以放到一个文件管理,但是代码量过多,不利于管理)
- Redux Toolkit包旨在成为编写Redux逻辑的标准方式,从而解决上面提到的问题
- 在很多地方为了称呼方便,也将之称为“RTK”
- 安装Redux Toolkit
npm install @reduxjs/toolkit react-redux
- Redux Toolkit的核心API主要是如下几个
configureStore:包装createStore以提供简化的配置选项和良好的默认值。它可以自动组合你的slice reducer,添加你提供的任何Redux中间件,redux-thunk默认包含,并启用Redux DevTools Extensionreducer,将slice中的reducer可以组成一个对象传入此处middleware:可以使用参数,传入其他的中间件devTools:是否配置devTools工具,默认为true
createSlice:接受reducer函数的对象、切片名称和初始状态值,并自动生成切片reducer,并带有相应的actionsname:用户标记slice的名词- 在之后的
redux-devtool中会显示对应的名词;
- 在之后的
initialState:初始化值- 第一次初始化时的值
reducers:相当于之前的reducer函数- 对象类型,并且可以添加很多的函数
- 函数类似于redux原来
reducer中的一个case语句 - 参数一:
state - 参数二:调用这个
action时,传递的action参数
- createSlice返回值是一个对象,包含所有的actions
createAsyncThunk: 接受一个动作类型字符串和一个返回承诺的函数,并生成一个pending/fulfilled/rejected基于该承诺分派动作类型的thunk- 当
createAsyncThunk创建出来的action被dispatch时,会存在三种状态pending:action被发出,但是还没有最终的结果fulfilled:获取到最终的结果(有返回值的结果)rejected:执行过程中有错误或者抛出了异常
- 当
接下来开始重构代码
代码结构
store | ├─index.js | ├─features | | ├─counter.js | | └home.js ├─pages ├─About.jsx ├─Home.jsx └Profile.jsx1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9store
// index.js import { configureStore } from "@reduxjs/toolkit" import counterReducer from "./features/counter" import homeReducer from "./features/home" const store = configureStore({ reducer: { counter: counterReducer, home: homeReducer } }) export default store1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14features
// counter.js import { createSlice } from "@reduxjs/toolkit" const counterSlice = createSlice({ name: "counter", initialState: { counter: 888 }, reducers: { addNumber(state, { payload }) { state.counter = state.counter + payload }, subNumber(state, { payload }) { state.counter = state.counter - payload } } }) export const { addNumber, subNumber } = counterSlice.actions export default counterSlice.reducer1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20// home.js import { createSlice, createAsyncThunk } from '@reduxjs/toolkit' import axios from 'axios' export const fetchHomeMultidataAction = createAsyncThunk( "fetch/homemultidata", async (extraInfo, { dispatch, getState }) => { // console.log(extraInfo, dispatch, getState) // 1.发送网络请求, 获取数据 const res = await axios.get("http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata") // 2.取出数据, 并且在此处直接dispatch操作(可以不做) const banners = res.data.data.banner.list const recommends = res.data.data.recommend.list dispatch(changeBanners(banners)) dispatch(changeRecommends(recommends)) // 3.返回结果, 那么action状态会变成fulfilled状态 return res.data }) const homeSlice = createSlice({ name: "home", initialState: { banners: [], recommends: [] }, reducers: { changeBanners(state, { payload }) { state.banners = payload }, changeRecommends(state, { payload }) { state.recommends = payload } }, // 异步请求也可以通过以下方法来订阅fetchHomeMultidataAction的状态 // 来改变state extraReducers: { // [fetchHomeMultidataAction.pending](state, action) { // console.log("fetchHomeMultidataAction pending") // }, // [fetchHomeMultidataAction.fulfilled](state, { payload }) { // state.banners = payload.data.banner.list // state.recommends = payload.data.recommend.list // }, // [fetchHomeMultidataAction.rejected](state, action) { // console.log("fetchHomeMultidataAction rejected") // } } extraReducers: (builder) => { // builder.addCase(fetchHomeMultidataAction.pending, (state, action) => { // console.log("fetchHomeMultidataAction pending") // }).addCase(fetchHomeMultidataAction.fulfilled, (state, { payload }) => { // state.banners = payload.data.banner.list // state.recommends = payload.data.recommend.list // }) } }) export const { changeBanners, changeRecommends } = homeSlice.actions export default homeSlice.reducer1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
pages
// About.jsx import React, { PureComponent } from 'react' import { connect } from "../hoc" import { addNumber } from "../store/features/counter" export class About extends PureComponent { render() { const { counter } = this.props return ( <div> <h2>About Counter: {counter}</h2> </div> ) } } const mapStateToProps = (state) => ({ counter: state.counter.counter }) const mapDispatchToProps = (dispatch) => ({ addNumber(num) { dispatch(addNumber(num)) } }) export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(About)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28// Home.jsx import React, { PureComponent } from 'react' // import axios from "axios" import { connect } from "react-redux" import { addNumber } from '../store/features/counter' import { fetchHomeMultidataAction } from '../store/features/home' // import store from "../store" // import { changeBanners, changeRecommends } from '../store/features/home' export class Home extends PureComponent { componentDidMount() { this.props.fetchHomeMultidata() // axios.get("http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata").then(res => { // const banners = res.data.data.banner.list // const recommends = res.data.data.recommend.list // store.dispatch(changeBanners(banners)) // store.dispatch(changeRecommends(recommends)) // }) } addNumber(num) { this.props.addNumber(num) } render() { const { counter } = this.props return ( <div> <h2>Home Counter: {counter}</h2> <button onClick={e => this.addNumber(5)}>+5</button> <button onClick={e => this.addNumber(8)}>+8</button> <button onClick={e => this.addNumber(18)}>+18</button> </div> ) } } const mapStateToProps = (state) => ({ counter: state.counter.counter }) const mapDispatchToProps = (dispatch) => ({ addNumber(num) { dispatch(addNumber(num)) }, fetchHomeMultidata() { dispatch(fetchHomeMultidataAction({name: "hyh", age: 18})) } }) export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(Home)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
# Redux Toolkit的数据不可变性
在React开发中,总是会强调数据的不可变性
- 无论是类组件中的state,还是redux中管理的state
- 事实上在整个JavaScript编码过程中,数据的不可变性都是非常重要的
所以在前面我们经常会进行浅拷贝来完成某些操作,但是浅拷贝事实上也是存在问题的
- 比如过大的对象,进行浅拷贝也会造成性能的浪费
- 比如浅拷贝后的对象,在深层改变时,依然会对之前的对象产生影响
事实上Redux Toolkit底层使用了immerjs的一个库来保证数据的不可变性
在coderwhy公众号的一片文章中也有专门讲解
immutable-js库的底层原理和使用方法为了节约内存,又出现了一个新的算法:Persistent Data Structure(持久化数据结构或一致性数据结构)
- 用一种数据结构来保存数据
- 当数据被修改时,会返回一个对象,但是新的对象会尽可能的利用之前的数据结构而不会对内存造成浪费
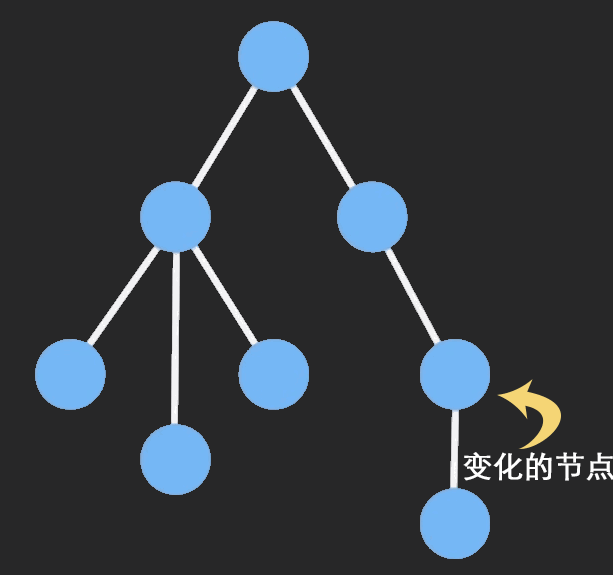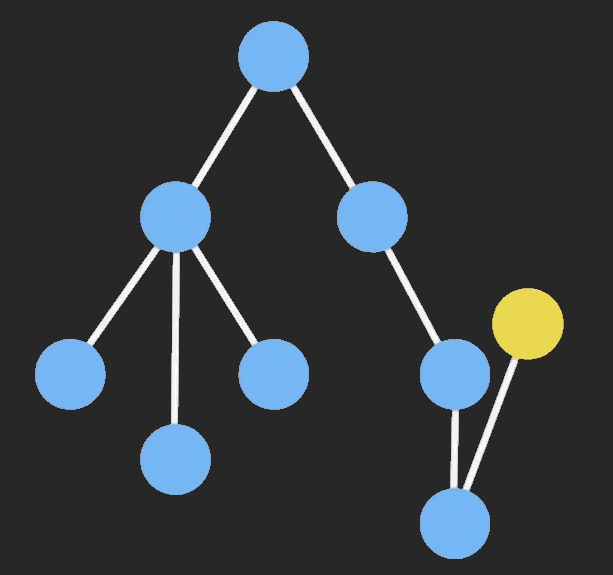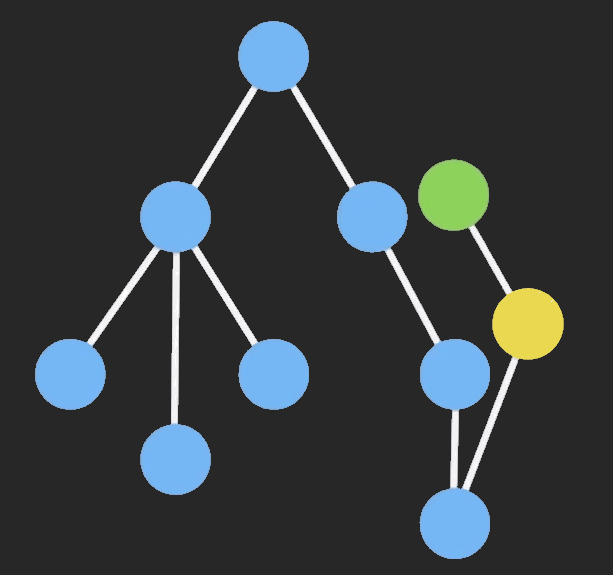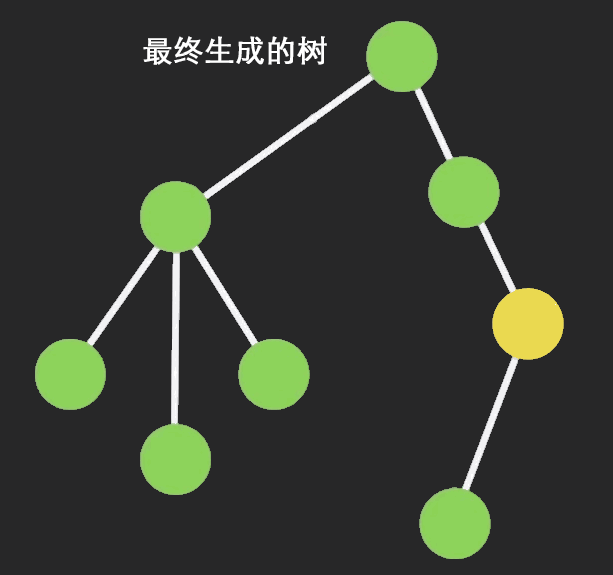
# 自定义connect函数
结构
hoc ├─StoreContext.js ├─connect.js └index.js1
2
3
4index.js
export { StoreContext } from "./StoreContext" export { connect } from "./connect"1
2connect.js
// connect的参数: // 参数一: 函数 // 参数二: 函数 // 返回值: 函数 => 高阶组件 import { PureComponent } from "react"; import { StoreContext } from "./StoreContext"; // import store from "../store" export function connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps, store) { // 高阶组件: 函数 return function(WrapperComponent) { class NewComponent extends PureComponent { constructor(props, context) { super(props) // 这里context就是store this.state = mapStateToProps(context.getState()) } componentDidMount() { this.unsubscribe = this.context.subscribe(() => { // this.forceUpdate() this.setState(mapStateToProps(this.context.getState())) }) } componentWillUnmount() { this.unsubscribe() } render() { const stateObj = mapStateToProps(this.context.getState()) const dispatchObj = mapDispatchToProps(this.context.dispatch) return <WrapperComponent {...this.props} {...stateObj} {...dispatchObj}/> } } // 这里会使用StoreContext的provider传入store的 NewComponent.contextType = StoreContext return NewComponent } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42StoreContext.js
import { createContext } from "react"; export const StoreContext = createContext()1
2
3使用: main.jsx
import React from 'react'; import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client'; // import { Provider } from "react-redux" import { StoreContext } from "./hoc" import App from './App'; import store from './store'; const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root')); root.render( // <React.StrictMode> // <Provider store={store}> // 这里使用自己封装的provider <StoreContext.Provider value={store}> <App /> </StoreContext.Provider> // </Provider> // </React.StrictMode> );1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 中间件 (Middleware)
打印日志需求
// log.js function log(store) { const next = store.dispatch function logAndDispatch(action) { console.log(11); console.log("当前派发的action:", action) // 真正派发的代码: 使用之前的dispatch进行派发 next(action) console.log("派发之后的结果:", store.getState()) } // monkey patch: 猴补丁 => 篡改现有的代码, 对整体的执行逻辑进行修改 store.dispatch = logAndDispatch } export default log1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16thunk需求
// thunk.js function thunk(store) { // 这里拿到的是上一个log中间件处理完之后的dispatch, 并不是store原始的 const next = store.dispatch function dispatchThunk(action) { console.log(22); if (typeof action === "function") { action(store.dispatch, store.getState) } else { next(action) } } store.dispatch = dispatchThunk } export default thunk1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16合并中间件
// applyMiddleware.js function applyMiddleware(store, ...fns) { fns.forEach(fn => fn(store)) } export default applyMiddleware1
2
3
4
5
6使用
import { createStore, compose, combineReducers } from "redux" import { log, thunk, applyMiddleware } from "./middleware" // import thunk from "redux-thunk" import counterReducer from "./counter" import homeReducer from "./home" import userReducer from "./user" // 将两个reducer合并在一起 const reducer = combineReducers({ counter: counterReducer, home: homeReducer, user: userReducer }) const store = createStore(reducer) applyMiddleware(store, log, thunk) export default store1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
